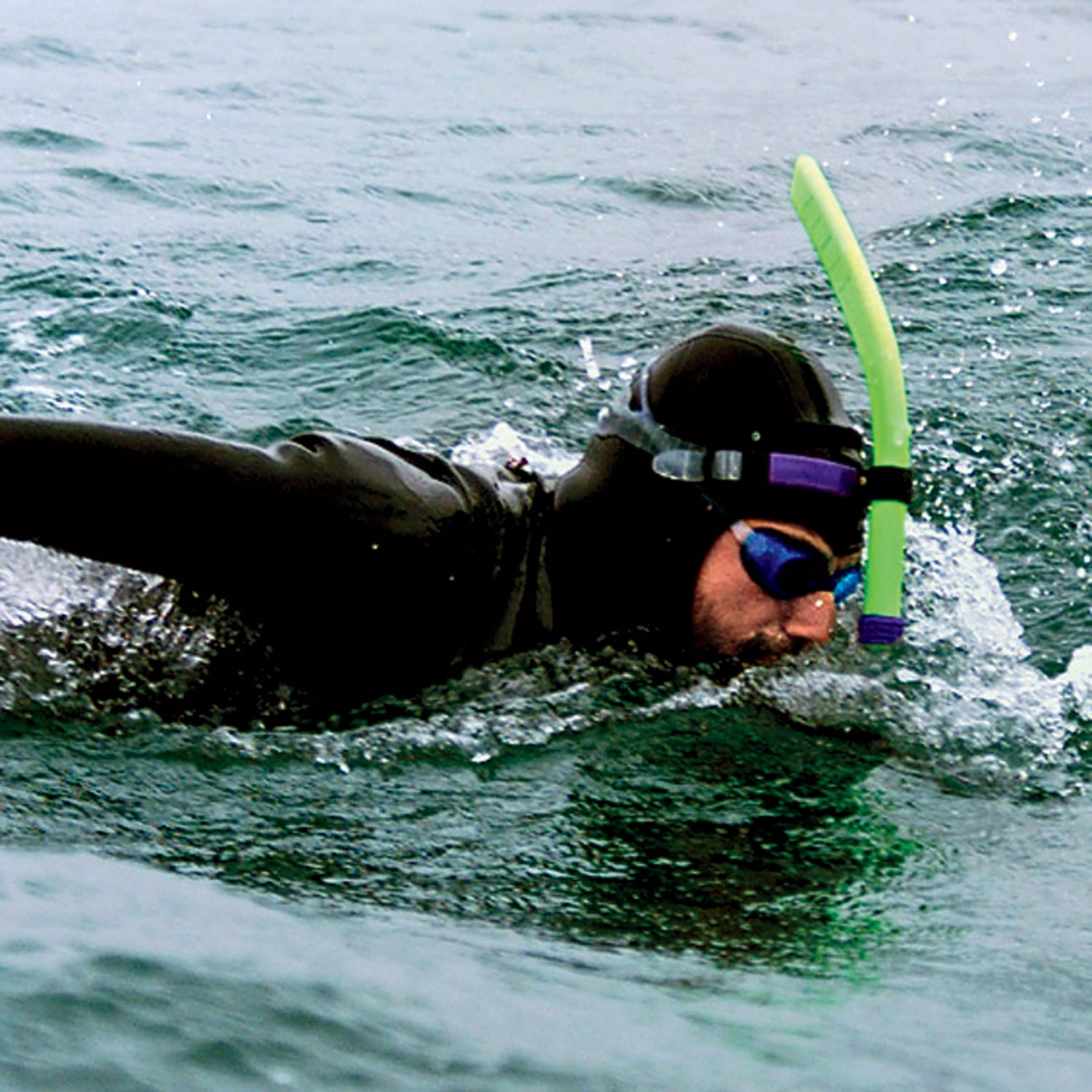
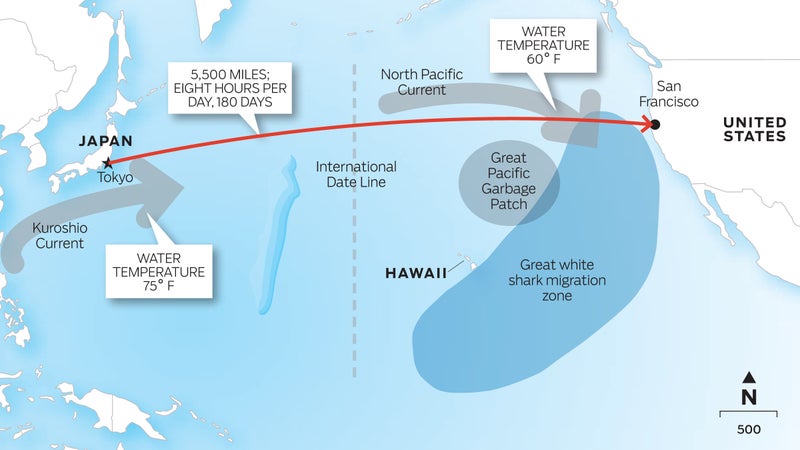
This spring, 47-year-old Frenchman Ben Lecomte will step into the Pacific Ocean in Japan and, over the next five months, attempt to become the first swimmer to cover the 5,500 miles to California. His plan: swim eight hours a day—using flippers and a snorkel but no flotation device—then rest for 16 hours on his support boat. We’d doubt his prospects if he hadn’t become the first person to swim 3,700 miles across the Atlantic in 1998.
But just because Lecomte has one ocean under his belt doesn’t mean the voyage is without risks.
The Route
Waves
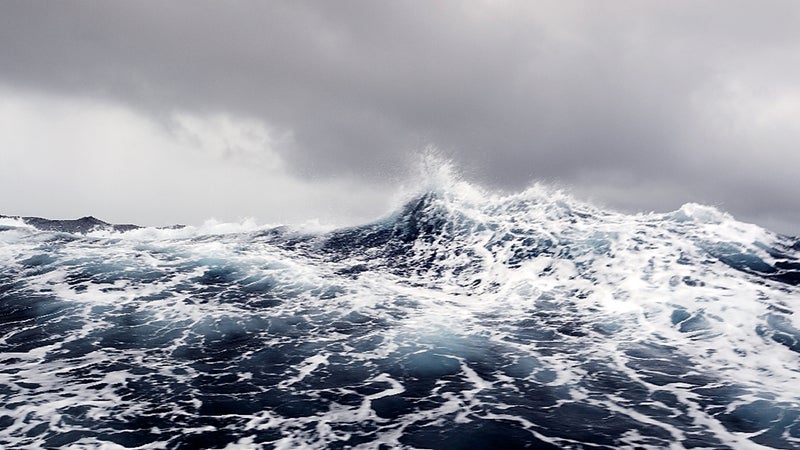

“You can swim in big waves as long as they don’t crash on you and keep you underwater for too long,” says Lecomte, who encountered 30-foot swells while crossing the Atlantic. And because his support boat’s electromagnetic field extends only about 20 feet (see “Sharks,” below), Lecomte has to stay close—and risk being dashed against the hull.
Exhaustion

The six-person support crew can pull him on board if he suffers physical fatigue, but mental fatigue is of equal concern. To stay alert during his shifts in the water, Lecomte will do a series of mental exercises, including counting and remembering family vacations. “The goal is to have your body on auto-pilot and your mind somewhere else,” he says. “When you lose that, that’s when the trouble starts.”
Sharks
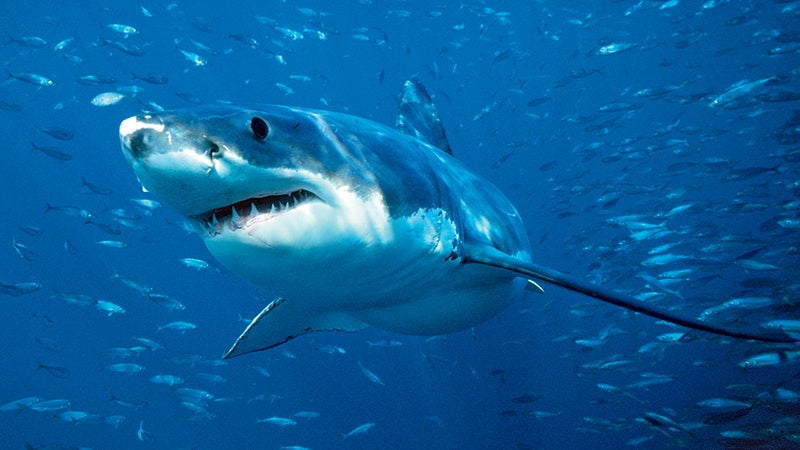

When Lecomte crossed the Atlantic, a blue shark followed him for five days. In the Pacific, he’ll face the ocean’s most fearsome apex predator—the great white. To hold the sharks off, Lecomte’s support boat emits an electromagnetic field that acts as a deterrent. Says Lecomte, “It’s not a matter of if I’ll encounter sharks, it’s a matter of when.”
The Cold
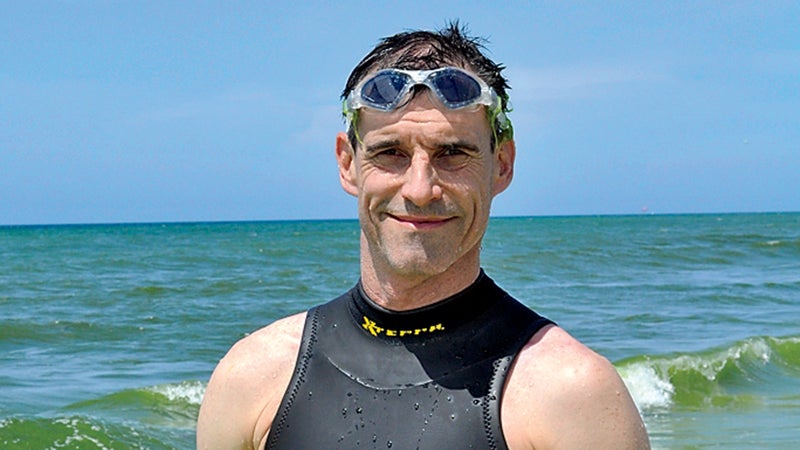

Lecomte could face water temperatures below 60 degrees. To fend off hypothermia, he’ll wear up to four two-millimeter wetsuits.


